Thermal Comfort
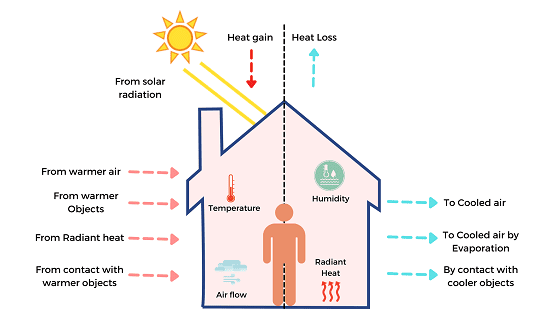
Thermal Comfort- Thermal comfort refers to the condition of mind that expresses satisfaction with the thermal environment. In simpler terms, it’s how comfortable or uncomfortable you feel with the temperature around you. Here’s a breakdown of key factors: In essence, thermal comfort is about creating an environment where people feel neither too hot nor too cold, allowing them to focus and be productive. What is Required Thermal Comfort “Required thermal comfort” generally refers to the minimum level of thermal comfort that is necessary or expected in a given situation. This level can vary depending on several factors, including: Key Considerations for “Required Thermal Comfort” In essence, “required thermal comfort” aims to provide a comfortable and healthy environment for building occupants while considering the specific needs and constraints of the situation. Who is Required Thermal Comfort Courtesy: The Engineering Mindset “Required thermal comfort” is essentially needed by anyone who occupies a built environment. This includes: In short, anyone who spends time indoors needs a thermally comfortable environment for their well-being, productivity, and overall quality of life. When is Required Thermal Comfort Required thermal comfort is needed whenever people are occupying a built environment. This includes: Essentially, required thermal comfort is an ongoing need whenever people are indoors. Where is Required Thermal Comfort Required thermal comfort is needed in any built environment where people spend time. This includes: Essentially, any space that is designed for human occupancy requires consideration of thermal comfort to ensure a healthy and productive environment. How is Required Thermal Comfort Courtesy: Saint-Gobain Architecture Student Contest Required thermal comfort is achieved through a combination of factors and technologies: 1. Building Design and Construction: 2. Heating and Cooling Systems: 3. Building Automation and Control Systems: 4. Occupant Behavior: By carefully considering these factors, it’s possible to create built environments that provide the required level of thermal comfort for occupants. Case Study on Thermal Comfort Thermal Comfort in a Modern Office Building Background: A large multinational corporation recently moved into a newly constructed, state-of-the-art office building in a temperate climate. The building boasts a sleek glass facade, advanced HVAC systems, and a focus on energy efficiency. However, within weeks, numerous employee complaints arose regarding thermal discomfort. Observations: Investigation: Findings: Recommendations: Conclusion: This case study highlights the importance of a holistic approach to achieving thermal comfort in modern buildings. By carefully considering factors such as building design, HVAC system performance, and occupant needs, it is possible to create comfortable and productive indoor environments while minimizing energy consumption. Note: This is a simplified case study for illustrative purposes. Real-world case studies would involve more detailed analysis, data collection, and potential implementation of more complex solutions. White paper on Thermal Comfort Achieving Thermal Comfort in Built Environments 1. Introduction Thermal comfort is a critical aspect of human well-being and productivity in built environments. It refers to the condition of mind that expresses satisfaction with the thermal environment. This white paper explores the key factors influencing thermal comfort, strategies for achieving it, and its significance in contemporary building design. 2. Factors Influencing Thermal Comfort Several factors interact to determine an individual’s thermal sensation: 3. Achieving Thermal Comfort Strategies for achieving thermal comfort include: 4. Importance of Thermal Comfort 5. Conclusion Achieving thermal comfort in built environments is essential for human well-being, productivity, and sustainability. By understanding the factors that influence thermal sensation and implementing appropriate strategies, building designers and occupants can create spaces that are both comfortable and energy-efficient. 6. Future Directions Note: This is a general overview of thermal comfort. Specific applications and considerations will vary depending on the type of building, climate, and occupant needs. References This white paper provides a foundational understanding of thermal comfort. For more detailed information and specific applications, readers are encouraged to consult relevant standards, research articles, and expert resources. Industrial Application of Thermal Comfort Courtesy: Polimi OpenKnowledge In industrial settings, thermal comfort is crucial for: Specific Applications: Strategies for Achieving Thermal Comfort in Industrial Settings: Key Considerations: By prioritizing thermal comfort in industrial settings, organizations can improve worker safety, enhance productivity, and create a more sustainable and efficient work environment. References